10 Cancers Associated with Obesity
To understand why extra fat becomes extra risky and why losing just a few kilos could well be the best health decision one could make, we need to delve into the understanding of the types of cancers that might be linked to obesity. This is a significant topic in cancer research, especially in studies published in journals with a cancer research impact factor of global relevance.
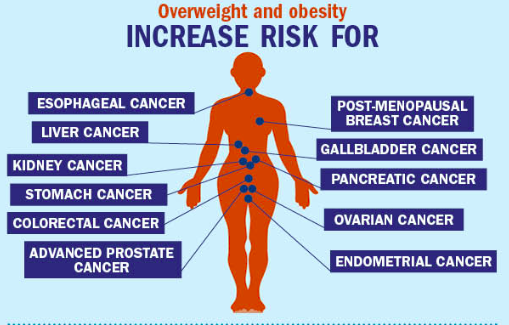
Breast Cancer (Postmenopausal Women)
It is said that women with obesity post-menopause are at least 20-40% more likely to develop this type. Fat cells produce estrogen, and in postmenopausal women, they become the main source of it. Excess estrogen goes along with an increased chance of mutations in breast cells, hence a higher chance of breast cancer. New evidence from cancer research indicates the role of cancer nutrition in mitigating some of these risks.
Colorectal Cancer
Obesity interferes with the hormones present in the gut, triggers inflammation, and causes insulin resistance. And all these throw the colon out of its rhythm. Accounts by the American Cancer Society reveal that obese people have a 30% higher chance of developing colorectal cancer. And yes, men seem to be more susceptible to this. Lifestyle and cancer diet interventions have shown promising results across different stage of cancer in related studies with a high cancer research impact factor.
Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer
Endometrial cancer is 2 to 4 times, even sometimes 7 times, more likely to happen in those women who have greater amounts of stored body fat. Just like in breast cancer, estrogen overproduction is the main culprit here, as it thickens the endometrial lining and nudges cells toward abnormal growth. Cancer research and cancer nutrition strategies are increasingly targeting hormone-related cancers like this one.
Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
So, the question arises here that how does obesity increase the chances of esophageal adenocarcinoma? The simple explanation for this is that an obese person, especially one with much abdominal fat, would have increased chances. For years, this acid reflux or GERD during this period has damaged the esophagus. This long-standing inflammation sets the stage for esophageal adenocarcinoma, which is one of the fastest-growing cancers in obese males. Several cancer research impact factor studies are investigating how cancer diet modifications can reduce acid reflux and inflammation in the esophagus.
Kidney (Renal Cell) Cancer
The kidneys filter your waste; nevertheless, too much weight might add to their workload. Obesity alternately affects kidney function, blood pressure, and insulin resistance. All these together increase your chances of renal cell carcinoma, the most common type of kidney cancer. Cancer research has shown how early changes in cancer nutrition can help regulate blood pressure and kidney health at any stage of cancer.
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer is deadly and sneaky; it gives off few early symptoms and shows a strong association with obesity. Fat tissue releases cytokines, which are inflammatory substances, and disrupts insulin levels; pancreatic cancer is the chaotic result of this chronic inflammation and excess insulin levels. Cancer research at the best medical oncology hospital in Delhi, impact factor publications consistently rank pancreatic cancer among the most critical areas where cancer diet plays a preventative role.
Gallbladder Cancer
Obesity is highly associated with gallstones, and gallstones increase the risk of gallbladder cancer. Fatty acids change bile production and induce chronic inflammation of the gallbladder. Women are at a greater risk of this rare but aggressive cancer, especially obese women. Understanding cancer nutrition in such cases helps formulate dietary strategies and early diagnosis across the stages of cancer.
Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma)
A liver, indeed, is the greatest detoxifying organ, but that cannot handle an overload of fats forever. Obesity causes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which progresses to cirrhosis and eventually to liver cancer. The obese are two times more likely to develop this kind of cancer than a person of a healthy weight. Being overweight thus increases the risk of being diagnosed with liver cancer. Advances in cancer research are supported by high cancer research impact factor studies.
Ovarian Cancer
This one goes on the tricky side and requires further exploration; however, indeed, emerging evidence has demonstrated that the obesity of women may actually elevate the risk of epithelial ovarian cancer, the most common form of the disease. Again, the hormonal activity of adipose tissue seems to enhance this risk along with chronic low-grade inflammation of low grade, an indicator of obesity. This puts it under the umbrella of ovarian cancer risk factors, which are now studied in-depth in cancer research journals.
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma, a disease of plasma cells in the bone marrow, has also been linked with high BMI. Researchers think that inflammatory factors and growth factors that are elevated in the obese might contribute to the abnormal growth of these cells. The risk is not colossal, but it certainly is statistically significant. A better understanding of cancer nutrition may aid in controlling progression through multiple stages of cancer.
The obese fat tissue in humans is not passive in storage; rather, it is an active tissue. It secretes hormones (including estrogen) and cytokines (inflammatory chemicals) that disrupt normal cell functioning, promote DNA damage, and support abnormal cell growth. Insulin resistance is another fallout of obesity, which in actuality facilitates the growth environment for cancer cells. Studies with high cancer research impact factors emphasise these mechanisms and the role of a proper cancer diet in interrupting them.
Losing a few pounds from your current weight can help prevent several types of cancer. In addition, physical activity strengthens the heart, promotes easier movement, benefits the mind and makes life more enjoyable. It’s not so much about having a “perfect figure” as it is about nurturing your body through mindful cancer nutrition and understanding ovarian cancer risk factors and others.
Cancer can affect you whether you are overweight or thin, as neither guarantees your safety. Nevertheless, obesity raises the risk factor. It is as if cancer gets new advantages to use in the game. If exercising regularly is still hard for you, if you don’t eat many vegetables or if greasy biryani is often your choice as dinner, this may serve as a reminder to look after your health sincerely. Your body and its organs will thank you when you decide to eat well and follow a preventive cancer diet. Hence, stay curious, show tenderness towards your body and keep yourself informed about your health. And for early diagnosis and treatment
Here are the top ten cancer hospitals in India, in no particular order:
1. Tata Memorial Hospital (TMH), Mumbai
The Pioneer & Public Sector Leader
Widely considered the best and most iconic cancer hospital in India. It is a government-funded institution under the Department of Atomic Energy.
- Why it’s top: Unmatched experience, massive patient volume, pioneering research, and highly subsidized care. It is a central hub for training and complex cancer surgeries.
- Key Specialty: Surgical Oncology, Radiation Oncology, and virtually all cancer types.
- Note: Due to high demand, waiting times can be long. It has a parallel private wing called ACTREC (Advanced Centre for Treatment, Research and Education in Cancer) in Navi Mumbai.
2. All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), Delhi
The Premier Medical Institute
While AIIMS is famous for all medical fields, its Department of Medical Oncology and Dr. B.R.A. Institute-Rotary Cancer Hospital (IRCH) within its campus is a state-of-the-art cancer care facility.
- Why it’s top: Integrates cutting-edge research with clinical care, attracts top medical talent, and handles the most complex cases.
- Key Specialty: Medical Oncology, Bone Marrow Transplants, and rare cancers.
3. The Cancer Institute (WIA), Adyar, Chennai
A Legacy of Compassionate Care
One of the oldest and most respected cancer centers in India, established in 1954. It combines free treatment for the underprivileged with world-class technology.
- Why it’s top: A model of non-profit oncology care, excellent outcomes, and a holistic approach to treatment.
- Key Specialty: Radiotherapy, Pediatric Oncology.
4. Apollo Hospitals, Chennai (& Multiple Locations)
Private Sector Giant with a Network
Apollo’s flagship unit in Chennai has one of the most advanced cancer care programs in the private sector. The network has comprehensive cancer centers across many major cities (Delhi, Bangalore, Hyderabad).
- Why it’s top: State-of-the-art technology (like Proton Therapy in Chennai), renowned surgeons, and a seamless multi-specialty approach.
- Key Specialty: Robotic Surgery, Proton Therapy, Bone Marrow Transplants.
5. Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute and Research Centre (RGCIRC), Delhi
Dedicated NCR Premier Center
One of Asia’s largest exclusive cancer hospitals, known for its high-volume care and excellent outcomes.
- Why it’s top: Focuses exclusively on oncology, offering super-specialized care. It has a strong team across all oncological disciplines.
- Key Specialty: Surgical Oncology, Uro-Oncology, and Hemato-Oncology.
6. Medanta – The Medicity, Gurugram
Quaternary Care with Top Talent
Founded by renowned cardiac surgeon Dr. Naresh Trehan, Medanta has a powerful Division of Oncology and Bone Marrow Transplant.
- Why it’s top: Brings a multi-specialty quaternary care model to cancer treatment, attracting leading oncologists from across the country.
- Key Specialty: Medical & Surgical Oncology, Nuclear Medicine (PET-CT), and complex multi-organ cases.
7. Fortis Memorial Research Institute (FMRI), Gurugram
Technology-Driven Care
A leading multi-specialty hospital known for its investment in the latest medical technology and diagnostics.
- Why it’s top: Houses advanced radiation technology (like CyberKnife, TomoTherapy) and a strong team for precision medicine and immunotherapy.
- Key Specialty: Radiation Oncology, Robotic Surgery.
8. HCG Cancer Centre, Bangalore (& Multiple Locations)
Largest Dedicated Cancer Network
HCG (HealthCare Global Enterprises) is focused exclusively on cancer care with a network of hospitals across India. Their Bangalore center is a flagship.
- Why it’s top: Entire ecosystem is designed around oncology, offering tailored treatments and access to numerous clinical trials.
- Key Specialty: Precision Oncology, Advanced Radiation Therapy.
9. Max Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, Delhi
Comprehensive Super-Specialty Care
Part of the Max Healthcare network, the Saket unit has a robust and well-regarded oncology department offering full-spectrum care.
- Why it’s top: Strong multi-disciplinary tumor boards, advanced surgical capabilities, and good patient support systems.
- Key Specialty: Organ-specific oncology programs (e.g., breast, lung, GI).
10. Artemis Hospital, Gurugram
Center of Excellence in Oncology
Known for its advanced infrastructure and patient-centric care in the Delhi-NCR region.
- Why it’s top: Offers a wide range of advanced treatments including robotic surgery, stereotactic radiosurgery, and haploidentical BMTs.
- Key Specialty: Surgical Oncology, Bone Marrow Transplant.
How to Choose the Right Hospital for You:
Specialization: Identify hospitals best for your specific cancer type (e.g., pediatric, blood-related, solid tumors).
Doctor’s Expertise: The specific oncologist (medical, surgical, radiation) is often more important than the hospital itself. Research their experience with your condition.
Technology: Ensure the hospital has the required technology for your proposed treatment (e.g., PET-CT, CyberKnife, Robotic Surgery).
Multidisciplinary Approach: The best care comes from a team of medical, surgical, and radiation oncologists working together.
Location and Cost: Consider logistics for long-term treatment. Get detailed cost estimates and check insurance/package applicability.



Leave Your Comment